What Relationship Do Red Blood Cells Have to Glucose Readings
Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, are the about abundant cells in the bloodstream and contains hemoglobin, the chemical compound that carries oxygen through the body. While hemoglobin can occur in a free state in some animals, in the human body information technology has to exist contained within a cell – the red blood cell. Whatsoever disruption of the cherry-red blood cells, its quantity, shape, size, structure or life cycle tin can therefore affect the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
Functions of Red Blood Cells
Apart from conveying oxygen, which is the master function of red blood cell, information technology can also conduct the following functions.
- Release the enzyme carbonic anhydrase which allows water in the blood to carry carbon dioxide to the lungs where it is expelled.
- Control the pH of the claret by acting as an acrid-base buffer.
Shape and Size of a Carmine Blood Cell
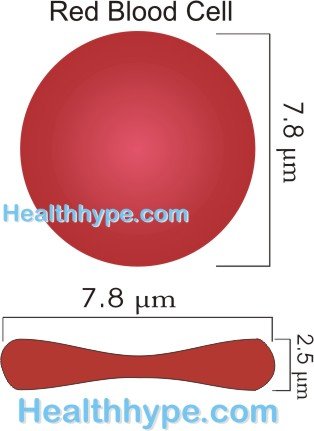
A red blood jail cell is a biconcave disc. But it is a round ball that is squeezed from 2 contrary ends to appear, widest at the sides and narrowest in the middle.
A cerise blood jail cell measures nearly 6 to eight micrometers in bore (average = seven.8 um) with an average thickness of 2 micrometers (2.five um at the thickest point and less than 1um at the center). Although a red blood cell is wider than some capillaries, its flexibility allows it to become distorted as information technology squeezes through narrow passages and so restores to its original shape.
Quantity of Red Blood Cells in the Human Body
The average male person adult has well-nigh 5 million red blood cells per cubic millimeter of claret, while the average female person adult has about 4.5 1000000 red claret cells per cubic milliliter of blood. This may vary by well-nigh 300,000 to 500,000 red blood cells. The number of cerise blood cells may vary depending on geographical location – a person who lives in high altitudes will have more red blood cells.
Picture from Wikimedia Eatables
Structure of Scarlet Blood Cells
Red claret cells have an unusual structure compared to other cells in the human being body. It lacks a nucleus, mitochondria or endoplasmic reticulum. Withal enzymes within the red blood cells allow it to produce small amounts of energy (ATP from glucose). The most important part of a red blood cell is hemoglobin, which is substantially the functional component of the cell.
Hemoglobin Structure
Hemoglobin is the molecule that is responsible for the oxygen carrying capacity of a red claret cell. It as well gives these cells a cerise color and is a combination of heme and globin. Heme is formed when succinyl-CoA binds with glycine to form a pyrrole molecule. Iv of these pyrrole molecules combine to form protoporphyrin IX which binds with iron to form the heme molecule. Globin is a long polypeptide chain.
When a heme molecule and globin molecule combine, it forms a hemoglobin chain. There may be slight variations in the hemoglobin chains designated as alpha, beta, gamma and delta chains. Four of these bondage need to combine to course the last hemoglobin molecule and the virtually common combination in the human torso, termed hemoglobin A, is made up of two alpha and two beta chains.
Each iron molecule can bind with one oxygen molecule, which contains ii oxygen atoms. Since each hemoglobin chain has one iron atom and each hemoglobin molecule has four bondage and therefore 4 iron molecule,s each hemoglobin molecule can conduct 8 oxygen atoms.
Every 100 milliters of blood, which contains diverse blood components, has nigh most 15 grams of hemoglobin.
Life Bicycle of Scarlet Blood Cells
Red claret cells are manufactured from the hemopoietic stalk cells in the bone marrow. These cells are are known as erythtropietic bone marrow cells and are partially differentiated. When ruddy blood cells accept to exist manufactured, these cells become through various phases of development until the mature ruby blood cell can exist released into the bloodstream. The final phase of maturation requires two important vitamins – vitamin B12 and folic acid. This procedure of developing from erythropoietic bone marrow cells to mature red blood cells takes virtually seven days.
The stimulus for producing red blood cells is hypoxia (low oxygen country). However, hypoxia alone will not be sufficient to trigger the production of new cherry-red blood cells unless the hormone erythropoietin is circulating in the bloodstream. This hormone is primarily produced by the kidneys. The process of manufacturing red blood cells in known every bit eryrthropoiesis.
The life span of a red blood cell is approximately 120 days but may exist removed out of circulation at any time if it is severely damaged and non-functional. Nigh of the carmine blood cells self destruct rather than being actively removed from the circulation and destroyed. The primary site where this occurs is in the spleen.
Once a red blood prison cell ruptures, hemoglobin is released into the circulation for processing. This is primarily done by the Kupffer cells of the liver and macrophages in the spleen and bone marrow. These macrophages release iron which is carried past transferrin to the bone marrow where it tin can be reused for the product of new cherry-red blood cells. The remaining porphyrin portion of the hemeglobin molecule is converted to bilirubin past the macrophages. The liver cells (hepatocytes) take upwardly the bilirubin, conjugate it and release information technology in the bile.
Source: https://www.healthhype.com/red-blood-cells-functions-size-structure-life-cycle-pictures.html
Post a Comment for "What Relationship Do Red Blood Cells Have to Glucose Readings"